Training Course on Georeferencing and Spatial Alignment Techniques
Training Course on Georeferencing and Spatial Alignment Techniques is designed to equip professionals with the essential skills to transform raw, unreferenced data into precise, actionable geographic information.
Course Overview
Training Course on Georeferencing and Spatial Alignment Techniques
Introduction
In today's data-driven world, the ability to accurately georeference and perform spatial alignment is paramount for unlocking the true potential of geospatial data. Training Course on Georeferencing and Spatial Alignment Techniques is designed to equip professionals with the essential skills to transform raw, unreferenced data into precise, actionable geographic information. Participants will delve into core GIS principles, master advanced geospatial techniques, and gain hands-on experience with industry-standard software, ensuring they can confidently integrate diverse datasets and produce accurate maps for informed decision-making.
The demand for professionals proficient in geospatial analysis, remote sensing, and spatial data management is rapidly expanding across various sectors. This course addresses this critical need by providing a comprehensive understanding of how to correctly position and orient spatial information, whether it's historical scanned maps, aerial imagery, or drone data. Through practical exercises and real-world case studies, attendees will learn to overcome common data quality issues, select appropriate coordinate reference systems (CRS), and apply advanced transformation algorithms to achieve highly accurate and reliable spatial datasets, crucial for urban planning, environmental monitoring, and resource management.
Course Duration
5 days
Objectives
- Grasp the foundational concepts of Geographic Information Systems and their applications.
- Identify, select, and manage appropriate CRS and datum transformations for various datasets.
- Accurately align scanned maps, aerial photographs, and satellite imagery to real-world coordinates.
- Integrate and align disparate vector datasets for seamless spatial analysis.
- Utilize various mathematical transformations (e.g., affine, polynomial, rubber sheeting) for optimal data alignment.
- Effectively select, capture, and manage GCPs for precise georeferencing.
- Evaluate and quantify the accuracy of georeferenced data using statistical methods and visual inspection.
- Identify and resolve challenges related to data quality, projection mismatches, and distortions.
- Import, export, and manage various geospatial data formats (e.g., GeoTIFF, Shapefile, CAD).
- Georeference and align drone imagery and other remote sensing products for mapping and analysis.
- Implement robust QC workflows to ensure the consistency and reliability of spatial data.
- Leverage georeferencing for practical applications in urban planning, environmental management, and disaster response.
- Explore basic scripting or model building for automating repetitive georeferencing tasks.
Organizational Benefits
- Enhance the precision and reliability of all spatial data, leading to better decision-making and reduced errors.
- Seamlessly combine diverse datasets from various sources, facilitating comprehensive geospatial analysis.
- Streamline workflows by automating repetitive georeferencing tasks and minimizing manual adjustments.
- Mitigate the risks associated with inaccurate spatial data, such as costly project rework or flawed planning.
- Optimize resource allocation and management through accurate mapping and spatial insights.
- Support robust urban planning, infrastructure development, and environmental impact assessments with high-quality geographic information.
- Build in-house expertise in cutting-edge geospatial technologies, positioning the organization as a leader in data-driven solutions.
- Foster better collaboration among teams by ensuring all stakeholders are working with accurately aligned geographic information.
Target Audience
- GIS Analysts and Specialists
- Cartographers and Map Producers.
- Remote Sensing Professionals.
- Urban Planners and Architects.
- Environmental Scientists and Conservationists.
- Surveyors and Geomatics Engineers
- Data Scientists and Analysts
- Researchers and Academics
Course Modules
Module 1: Fundamentals of Georeferencing and GIS Basics
- Introduction to GIS and Spatial Data: Understanding the nature of geographic information, types of spatial data (raster and vector), and the importance of location.
- Coordinate Systems and Projections: Delving into geographic and projected coordinate systems, datums, and the impact of map projections on spatial accuracy.
- Data Acquisition and Sources: Overview of how spatial data is collected (GPS, remote sensing, digitization of analog maps) and common data formats.
- Introduction to Georeferencing Concepts: Defining georeferencing, its purpose, and the fundamental principles of aligning unreferenced data.
- Case Study: Examining historical map datasets requiring georeferencing for historical urban development analysis.
Module 2: Raster Georeferencing Techniques
- Setting Up the Georeferencing Environment: Tools and functionalities within GIS software for raster georeferencing.
- Identifying and Placing Ground Control Points (GCPs): Strategies for selecting accurate and well-distributed GCPs from reference data.
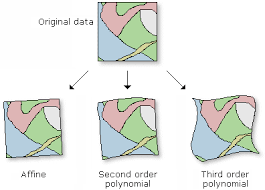
- Transformation Methods (Polynomial, Affine): Understanding different mathematical models for transforming raster data and their applications.
- Evaluating Georeferencing Accuracy: Residual errors, Root Mean Square (RMS) error, and visual inspection techniques.
- Case Study: Georeferencing scanned engineering plans for integration into a new infrastructure project.
Module 3: Advanced Raster Alignment and Distortion Handling
- Rubber Sheeting and Spline Transformations: Advanced techniques for correcting localized distortions in complex or highly warped raster images.
- Image Rectification and Orthorectification: Understanding the process of removing geometric distortions caused by terrain and sensor tilt.
- Working with Mismatched Projections: Strategies for reprojecting and transforming rasters between different coordinate systems.
- Georeferencing Aerial and Satellite Imagery: Specific considerations and best practices for aligning high-resolution imagery.
- Case Study: Correcting distortions in old aerial photographs for environmental change detection over several decades.
Module 4: Vector Spatial Alignment and Data Integration
- Vector Data Alignment Principles.
- Snapping and Topology Rules
- Attribute Table Management and Joining: Integrating non-spatial attribute data with georeferenced spatial features.
- Spatial Joins and Overlays: Combining information from different vector layers based on their spatial relationships.
- Case Study: Aligning disparate cadastral maps with existing road networks for property management and urban planning.
Module 5: Georeferencing Drone and UAV Data
- Introduction to Drone Data Acquisition
- Photogrammetry Basics for Georeferencing
- Ground Control Points (GCPs) for Drone Data
- Processing Drone Imagery for Georeferencing
- Case Study: Georeferencing drone-captured imagery for agricultural field analysis and precision farming.
Module 6: Quality Control and Data Validation
- Establishing Quality Control Workflows: Developing systematic approaches for ensuring spatial data quality.
- Accuracy Assessment and Error Reporting: Quantifying and reporting the positional accuracy of georeferenced datasets.
- Metadata Standards and Documentation: Importance of comprehensive metadata for understanding data lineage and quality.
- Troubleshooting and Problem Solving: Common challenges in georeferencing and practical solutions.
- Case Study: Implementing a QC protocol for a large-scale government mapping project to ensure data reliability for public use.
Module 7: Advanced Concepts and Automation in Georeferencing
- Georeferencing Unconventional Data: Techniques for aligning non-traditional spatial representations
- Introduction to Scripting for Georeferencing: Basic concepts of Python (ArcPy/PyQGIS) for automating simple georeferencing tasks.
- Batch Processing and Model Builder: Utilizing graphical model builders within GIS software for efficient batch georeferencing.
- Georeferencing in Web GIS Environments: Overview of georeferencing considerations for online mapping and web applications.
- Case Study: Automating the georeferencing of hundreds of historical building blueprints for a heritage preservation initiative.
Module 8: Applications and Future Trends in Georeferencing
- Georeferencing for Environmental Monitoring: Applications in disaster management, climate change studies, and natural resource assessment.
- Georeferencing in Urban and Regional Planning: Use in infrastructure development, zoning, and demographic analysis.
- Emerging Georeferencing Technologies: AI and machine learning for automated georeferencing, cloud-based solutions.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Data privacy, copyright, and responsible use of georeferenced data.
- Case Study: The role of accurate georeferencing in a rapid response flood mapping and damage assessment project.
Training Methodology
- Instructor-Led Presentations.
- Hands-on Practical Exercises
- Real-World Case Studies.
- Interactive Discussions and Q&A.
- Group Work and Collaborative Learning.
- Demonstrations.
- Continuous Feedback
Register as a group from 3 participants for a Discount
Send us an email: info@datastatresearch.org or call +254724527104
Certification
Upon successful completion of this training, participants will be issued with a globally- recognized certificate.
Tailor-Made Course
We also offer tailor-made courses based on your needs.
Key Notes
a. The participant must be conversant with English.
b. Upon completion of training the participant will be issued with an Authorized Training Certificate
c. Course duration is flexible and the contents can be modified to fit any number of days.
d. The course fee includes facilitation training materials, 2 coffee breaks, buffet lunch and A Certificate upon successful completion of Training.
e. One-year post-training support Consultation and Coaching provided after the course.
f. Payment should be done at least a week before commence of the training, to DATASTAT CONSULTANCY LTD account, as indicated in the invoice so as to enable us prepare better for you.