Training Course on Advanced Geocoding and Address Matching
Training Course on Advanced Geocoding and Address Matching focuses on developing a deep understanding of geospatial data quality, data standardization, and the various geocoding algorithms and tools available.
Course Overview
Training Course on Advanced Geocoding and Address Matching
Introduction
In today's data-driven world, location intelligence is paramount for optimizing operations, enhancing customer experiences, and making informed strategic decisions. This advanced training course delves into the intricate world of geocoding and address matching, equipping participants with the expertise to transform raw address data into precise, actionable geographic coordinates. We'll explore cutting-edge techniques and best practices, moving beyond basic geocoding to tackle complex challenges like data inconsistencies, fuzzy matching, and multi-source integration, ultimately empowering professionals to unlock the full potential of their geospatial data.
Training Course on Advanced Geocoding and Address Matching focuses on developing a deep understanding of geospatial data quality, data standardization, and the various geocoding algorithms and tools available. From rooftop accuracy to batch geocoding large datasets, attendees will gain hands-on experience in preparing, processing, and validating address information for diverse applications. By mastering these critical skills, participants will be able to significantly improve the accuracy of their spatial analyses, streamline workflows, and derive powerful insights for sectors ranging from logistics and urban planning to marketing and public health.
Course Duration
10 days
Course Objectives
- Understand core geocoding concepts, including forward and reverse geocoding, and their real-world applications.
- Implement data cleaning and standardization techniques for improved geocoding accuracy.
- Utilize fuzzy matching, phonetic algorithms, and machine learning for robust address resolution.
- Integrate geocoded data with various GIS platforms and databases for comprehensive analysis.
- Learn to build and configure geocoding locators and services for specific organizational needs.
- Efficiently process large datasets for scalable location intelligence initiatives.
- Assess match scores, confidence levels, and identify strategies for error resolution.
- Understand the importance of authoritative data sources and their impact on geocoding quality.
- Work with popular geocoding APIs dynamic geocoding.
- Apply geocoded data in spatial analysis, customer profiling, and market segmentation.
- Troubleshoot common issues like ambiguous addresses, multi-language support, and geospatial bias.
- Implement secure practices for handling and storing sensitive location data.
- Understand emerging technologies like AI in geocoding and real-time geocoding
Organizational Benefits
- Streamlines processes like route optimization, delivery management, and field service dispatch, leading to significant cost savings and faster operations.
- Reduces errors and inconsistencies in address data, leading to more reliable analyses and decision-making. This directly impacts data governance and compliance.
- Enables precise customer location analysis, allowing for targeted marketing campaigns, personalized service delivery, and improved customer relationship management (CRM).
- Provides a clear understanding of geographic distribution for assets, customers, or services, facilitating smarter planning for infrastructure, sales territories, and resource deployment. This supports strategic planning and market analysis.
- Improves fraud detection in industries like insurance by accurately assessing risk exposure based on location data.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations can leverage location intelligence to identify new opportunities, analyze competitor locations, and gain a distinct edge in the market.
- Ensures accurate reporting and adherence to location-based regulations, particularly in sectors like public safety and healthcare.
- Empowers data analysts and decision-makers with high-quality, spatially enabled data for more informed business intelligence (BI) and geographic information systems (GIS) applications.
Target Audience
- GIS Professionals & Analysts
- Data Scientists & Data Analysts.
- Urban Planners & Demographers
- Logistics & Supply Chain Managers.
- Marketing & Sales Managers
- Public Health Specialists
- Emergency Services Personnel.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Analysts.
Course Outline
Module 1: Introduction to Geocoding and Address Data
- Definition and Importance of Geocoding & Address Matching
- Types of Geocoding: Forward, Reverse, Batch, and Interactive
- Understanding Address Data Structures and Components
- Common Challenges in Address Data
- Case Study: Analyzing a large retail chain's customer address database to identify common data entry errors and their impact on market analysis.
Module 2: Geocoding Fundamentals and Principles
- Geographic Coordinate Systems
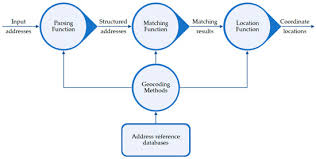
- Geocoding Process: Parsing, Standardization, Matching, Interpolation
- Reference Data: Street Networks, Parcel Data, Postal Codes
- Match Scores and Confidence Levels Explained
- Case Study: Comparing the accuracy of different geocoding methods for a public utility company needing precise service addresses.
Module 3: Data Preparation and Standardization for Geocoding
- Techniques for Data Cleaning and Validation
- Address Parsing and Component Extraction
- Normalization and Formatting Best Practices
- Handling Missing or Incomplete Address Information
- Case Study: Standardizing a legacy database of historical property records for a real estate firm to enable consistent mapping and analysis.
Module 4: Address Matching Algorithms and Techniques
- Exact Matching vs. Fuzzy Matching
- Phonetic Algorithms (e.g., Soundex, Metaphone)
- String Similarity Measures (e.g., Levenshtein Distance)
- Rule-Based and Dictionary-Based Matching
- Case Study: Implementing fuzzy matching algorithms to link customer records from various sources (e.g., online registrations, in-store purchases) with slight variations in address spelling for a telecommunications provider.
Module 5: Advanced Geocoding with GIS Software
- Creating and Managing Geocoding Locators/Services
- Configuring Geocoding Styles and Matching Parameters
- Single Address and Batch Geocoding Operations
- Reviewing and Refining Geocoding Results within GIS Environments
- Case Study: Geocoding a million customer addresses using ArcGIS Pro for a national insurance company to visualize policyholder distribution and risk exposure.
Module 6: Enterprise Geocoding Solutions and APIs
- Introduction to Cloud-Based Geocoding Services
- Understanding API Requests, Responses, and Rate Limits
- Integrating Geocoding APIs into Applications
- Cost Considerations and API Key Management
- Case Study: Developing a web application for a logistics company that uses a geocoding API to dynamically geocode delivery addresses entered by drivers.
Module 7: Reverse Geocoding and Point-in-Polygon Analysis
- Converting Coordinates to Addresses
- Applications of Reverse Geocoding
- Introduction to Point-in-Polygon and Spatial Joins
- Analyzing Spatial Relationships Between Geocoded Points and Polygons
- Case Study: Using reverse geocoding to identify the nearest police station or hospital for emergency calls based on incident coordinates, enhancing rapid response for a public safety agency.
Module 8: Geocoding for Spatial Analysis and Visualization
- Visualizing Geocoded Data on Maps
- Performing Spatial Queries and Selections
- Creating Drive-Time Polygons and Buffers
- Integrating Geocoded Data with Other Spatial Layers
- Case Study: A marketing firm uses geocoded customer addresses to create drive-time territories for new store locations and visualize customer density.
Module 9: Quality Assurance and Error Management in Geocoding
- Identifying and Resolving Unmatched Addresses
- Strategies for Improving Geocoding Match Rates
- Understanding Geocoding Error Codes and Messages
- Techniques for Manual Review and Correction
- Case Study: A government agency responsible for property taxation reviews unmatched addresses from their geocoding process and implements strategies to achieve higher match rates for accurate assessments.
Module 10: Advanced Topics in Reference Data and Maintenance
- Importance of High-Quality and Up-to-Date Reference Data
- Strategies for Acquiring and Maintaining Reference Datasets
- Dealing with Dynamic Addresses and New Developments
- Data Refresh Cycles and Versioning
- Case Study: A city planning department establishes a systematic process for updating its street network and parcel data to ensure accurate geocoding for zoning and permitting applications.
Module 11: Geocoding for Specific Industries and Applications
- Geocoding in Logistics and Transportation
- Geocoding for Marketing and Sales
- Geocoding in Public Safety and Emergency Response
- Geocoding for Urban Planning and Demographics
- Case Study: An e-commerce company uses advanced geocoding to optimize its delivery routes, reducing fuel costs and improving delivery times.
Module 12: Performance Optimization and Scalability
- Strategies for Optimizing Geocoding Performance
- Handling Large Volumes of Address Data Efficiently
- Parallel Processing and Distributed Geocoding
- Cloud Computing and Scalable Architectures
- Case Study: An electoral commission needs to geocode millions of voter registration records before an election. This module explores strategies to achieve this efficiently.
Module 13: Data Privacy, Security, and Ethical Considerations
- Regulations and Best Practices for Handling Location Data
- Anonymization and Aggregation of Geocoded Data
- Ethical Implications of Geocoding and Location Tracking
- Data Security Measures for Geospatial Databases
- Case Study: A healthcare provider discusses the ethical considerations and privacy safeguards when geocoding patient addresses for disease outbreak analysis.
Module 14: Emerging Trends in Geocoding and Location Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning in Geocoding
- Big Data and Real-time Geocoding
- Indoor Positioning and Geocoding
- Location-Based Services (LBS) and Future Applications
- Case Study: Exploring how a smart city initiative could leverage real-time geocoding of sensor data for dynamic traffic management and emergency response.
Module 15: Building a Comprehensive Geocoding Strategy
- Assessing Organizational Needs and Requirements
- Developing a Geocoding Workflow and Implementation Plan
- Choosing the Right Tools and Technologies
- Measuring ROI and Continuous Improvement
- Case Study: A national retail chain develops a comprehensive geocoding strategy to standardize all customer and store addresses, integrate with their CRM system, and improve targeted marketing campaigns.
Training Methodology
- Instructor-Led Sessions.
- Hands-on Labs and Exercises
- Case Study Analysis.
- Interactive Discussions.
- Demonstrations.
- Problem-Solving Workshops.
- Q&A.
- Resource Materials
Register as a group from 3 participants for a Discount
Send us an email: info@datastatresearch.org or call +254724527104
Certification
Upon successful completion of this training, participants will be issued with a globally- recognized certificate.
Tailor-Made Course
We also offer tailor-made courses based on your needs.
Key Notes
a. The participant must be conversant with English.
b. Upon completion of training the participant will be issued with an Authorized Training Certificate
c. Course duration is flexible and the contents can be modified to fit any number of days.
d. The course fee includes facilitation training materials, 2 coffee breaks, buffet lunch and A Certificate upon successful completion of Training.
e. One-year post-training support Consultation and Coaching provided after the course.
f. Payment should be done at least a week before commence of the training, to DATASTAT CONSULTANCY LTD account, as indicated in the invoice so as to enable us prepare better for you.